Iris Publishers - Current Trends in Clinical & Medical Sciences (CTCMS)
Active Filtering and Exchange of Indoor Air by Means of Mobile Air Conditioners to Avoid Infection by The SARS Cov-2 Virus
Authored by Sebastian König
Introduction
In not actively ventilated rooms
such as in schools, air exchange is insufficient, particularly during win- ter.
Under the presence of COVID-19 or to reduce the CO2 concentration, the air must
be filtered and refreshed as well as possible. A tracer clearance experiment
using a mobile air conditioner e.g. from KRONE Kälte + Klima VertriebsmbH
Germany is supposed to determine to what extent. In Szabadi [1]. the air
exchange rate [n] = 1/h is introduced as a measure of air exchange. The exhaust
volume flow [dV/dt] ⩒ = m3/h is related to room volume
[V] = m3. The air exchange rate n is a multiple of the room volume. Reference
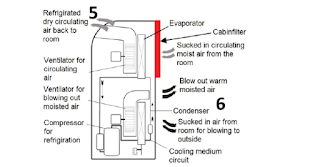
values are n = 3/h <= n <= 6/h. The air conditioner in (Figure 1)
comprises an air recirculation (5) and an active air exchange (6). The
recirculation may also filter and cool the air. Here, the air filter rate [f] =
1/h serves as a measure. Both measures must be considered according to [1].
Setup
A mobile air conditioner (1) in
(Figure 2) actively recirculates (2) and refreshes (3) the air of the room. A
ventilator (4) supports recirculation. The recirculation of air (5) in (Figure
1) also cools an dehumidifies and filters the air. The second air exchange (6)
suck in the room air and blows it out of the window. The air conditioner
GREE GPC-12-AL-R290 [2] comes with
a recirculation volume flow of ⩒ = 360 m3/h and is optimized for
rooms up to floor area of 22m2an air exchange rate of n ≈ 16/h. The conducted
measurements show effectiveness also in bigger rooms. Disco fog (EUROLITE smoke
fluid -X EXTREM A2) served as a tracer replacing the aerosol. The relative fog
density is measured indirectly via relative light transmission T = 0T=0%...100%
alternativly 0%<=T<=100% with measuring instrument TRDA 2.0 [3]. In a
seminar room of V = 220 m³ Figure 3, an active operating mode without
refrigeration and without dehumidification is used (Figure 1& 2).
Result
Figure 4 shows the plot of the
tracer clearance process by relative light transmission as a function of 83
minutes the fog is removed completely whence n = 360 m3/h /220 m3 = 1, 6/h.
After t < 10 s without fog (which is T˳ = 100%) the room is filled with fog.
The light transmission goes down Figure 4 shows the plot of the tracer
clearance process by relative light transmission as a function of two T <
10%. At the same time the air filter rate f = 2/h has effect. As example for
lecture rooms, n ≥ 8/h is required. This is accomplished by stationary air
conditioners. the step response of a simple mathematical model with just
one-time constant τ and a normalized light transmission T˳= 100% is plotted in
red in Figure
To read more about this article: https://irispublishers.com/ctcms/fulltext/active-filtering-and-exchange-of-indoor-air-by-means-of-mobile-air-conditioners.ID.000542.php
Indexing List of Iris Publishers: https://medium.com/@irispublishers/what-is-the-indexing-list-of-iris-publishers-4ace353e4eee
Iris
publishers google scholar citations: https://scholar.google.co.in/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=irispublishers&btnG=



Comments
Post a Comment